Best practices analysis
The PREVENTCKD consortium conducted the initial compilation using various key tools and methods.


Sources for best practices
• EU best practices portal
• PubMed
• Google Scholar
• consensus AI
• Stakeholder’s websites
• Partner’s database
Selection criteria
• Primary or secondary prevention initiatives on CKD
• Early detection or diagnosis initiatives, including population screening actions, with preference for those that have defined the results obtained.
• Actions that were replicable in different environments and situations.
• Studies, campaigns, initiatives that could demonstrate impact in their environments
• Actions that would delay the progression of CKD
• Early education initiatives for chronic kidney patients in the initial stages
• Identification of biomarkers for early diagnosis of CKD
• Early treatment and management of CKD
Results
The 104 initiatives were compiled into 6 groups:
• Group 1: scientific researches (RCT and nonRCT trials) and editorials.
• Group 2: clinical guides, handbooks and consensus protocols.
• Group 3: reports, bibliographic reviews.
• Group 4: awareness campaigns, actions with policymakers and other awareness activities.
• Group 5: educational programs, apps, websites, brochures, etc.
• Group 6: strategic documents, epidemiological researches and other organizational documents.
Conclusions

• CKD has risk factors and the underlying diseases that can cause it
• CKD has two very effective measures to calculate the state of the kidneys: the calculation of the albumin/creatinine/urea ratio and the estimation of the glomerular filtration rate.
• Tests determine key measurements are accessible to professionals: a simple urine analysis and a simple blood test
• Both tests are very cheap and affordable for any health system

• Lack of data about how people in risk perceive their risk, how to promote healthy habits, follow the medical recommendations, prescriptions…
• Lack of clear and integral guidelines for healthy lifestyle
• Lack of data about how affects emotional, coping styles, resilience etc. in adherence and healthy habits (nutrition and physical activity)
• Lack of data about the outcomes in awareness campaigns and actions with Policymakers
• Lack of real data in early stages of CKD (from Stage 1 to 4)
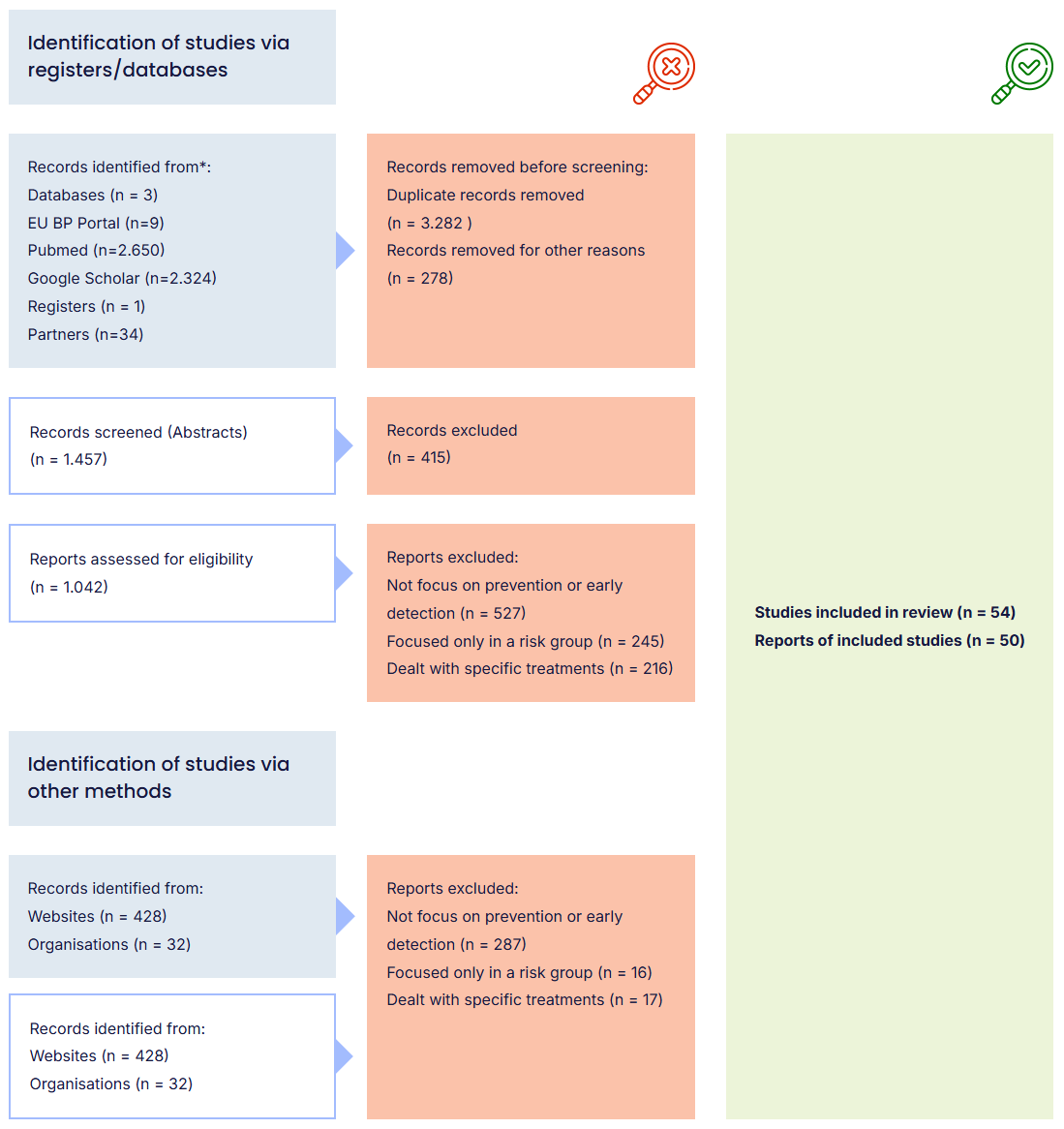
Prisma
Flow diagram
Records identified from*:
Databases (n = 3)
EU BP Portal (n=9)
Pubmed (n=2.650)
Google Scholar (n=2.324)
Registers (n = 1)
Partners (n=34)
Records removed before screening:
Duplicate records removed
(n = 3.282 )
Records removed for other reasons
(n = 278)
Records screened (Abstracts)
(n = 1.457)
Records excluded
(n = 415)
Reports assessed for eligibility
(n = 1.042)
Reports excluded:
Not focus on prevention or early detection (n = 527)
Focused only in a risk group (n = 245)
Dealt with specific treatments (n = 216)
Identification of studies via other methods
Records identified from:
Websites (n = 428)
Organisations (n = 32)
Records identified from:
Websites (n = 428)
Organisations (n = 32)
Reports excluded:
Not focus on prevention or early detection (n = 287)
Focused only in a risk group (n = 16)
Dealt with specific treatments (n = 17)
Studies included in review (n = 54)
Reports of included studies (n = 50)
Get In Touch
Contact us?